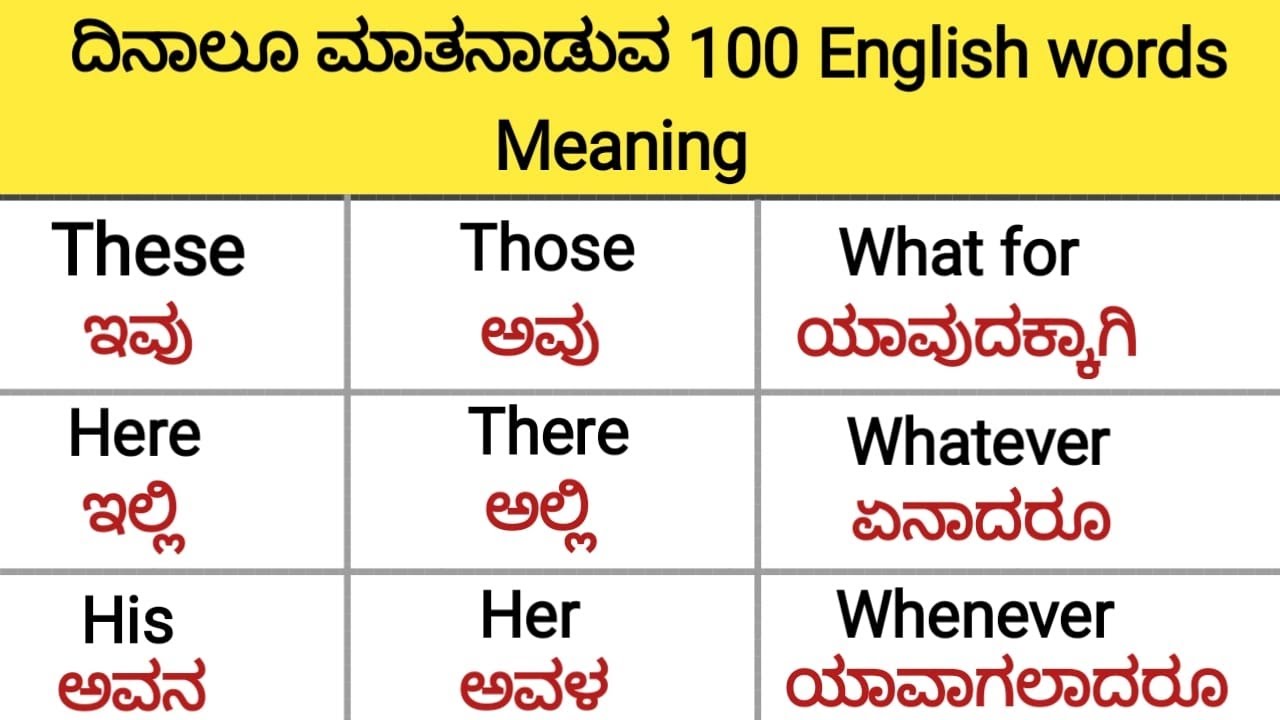
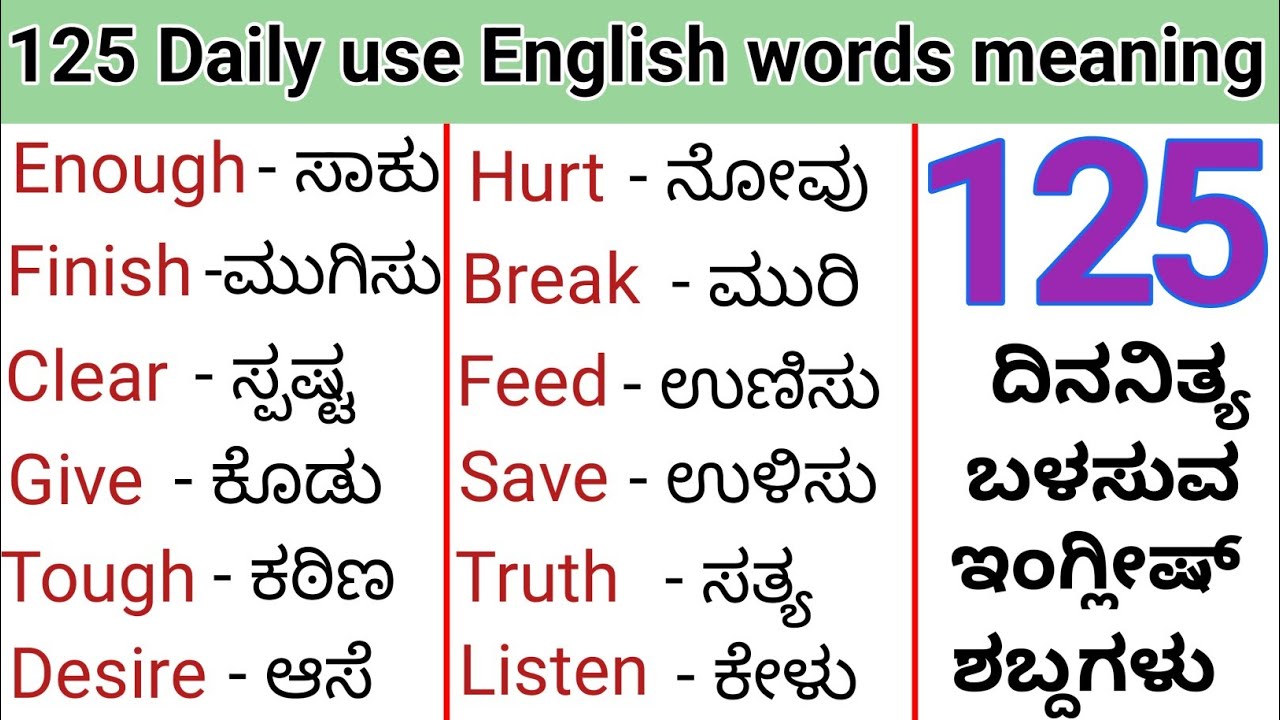
What does "interpreting meaning in Kannada" mean?
Understanding the meaning of a text or speech in Kannada.
Interpreting meaning in Kannada is the process of understanding the intended meaning of a text or speech in the Kannada language. This can involve understanding the literal meaning of the words, as well as the cultural and contextual factors that may influence the interpretation.
It is a complex and challenging task, as it requires a deep understanding of both the Kannada language and the culture in which it is used.
However, it is also a rewarding task, as it can provide a deep understanding of the Kannada language and culture, and can help to build bridges between different cultures.
Interpreting Meaning in Kannada
Interpreting meaning in Kannada involves understanding the intended meaning of a text or speech in the Kannada language. Here are seven key aspects to consider when interpreting meaning in Kannada:
- Cultural context: Kannada is a language spoken in the Indian state of Karnataka, and its meaning can be influenced by the culture and traditions of the region.
- Historical context: Kannada has a long and rich history, and its meaning can be influenced by historical events and movements.
- Literary context: Kannada is a literary language, and its meaning can be influenced by the works of Kannada poets and writers.
- Grammatical context: Kannada has a complex grammatical system, and its meaning can be influenced by the way words are structured and combined.
- Pragmatic context: Kannada is a spoken language, and its meaning can be influenced by the context in which it is used.
- Discourse context: Kannada is a discourse language, and its meaning can be influenced by the way it is used in conversation and other forms of discourse.
- Cognitive context: Kannada is a cognitive language, and its meaning can be influenced by the way it is processed and understood by the human mind.
These seven key aspects are essential for understanding the meaning of a text or speech in Kannada. By considering these aspects, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
1. Cultural context
The cultural context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. Kannada is spoken in the Indian state of Karnataka, which has a rich and diverse culture. The culture of Karnataka has been influenced by many factors, including the Dravidian, Indo-Aryan, and Islamic cultures. This has resulted in a unique and complex culture that is reflected in the Kannada language.
For example, the Kannada word "namaskara" means "hello" or "goodbye." However, the way that namaskara is said can convey different meanings. If it is said with a slight bow and a smile, it is a polite and respectful greeting. However, if it is said quickly and without any body language, it can be interpreted as a more casual greeting.
Another example is the Kannada word "anna." Anna means "brother" in Kannada. However, it can also be used as a term of respect for someone who is older than you. For example, you might call your teacher "anna" as a sign of respect.
Understanding the cultural context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the culture and traditions of Karnataka, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
2. Historical Context
The historical context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. Kannada has a long and rich history, and its meaning has been influenced by many historical events and movements.
- The rise and fall of empires: Kannada has been spoken in the region now known as Karnataka for over 2,000 years. During this time, the region has been ruled by many different empires, including the Kadambas, the Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, and the Vijayanagara Empire. Each of these empires has left its mark on the Kannada language, and their influence can still be seen in the language today.
- The influence of religion: Kannada has also been influenced by religion. The region has been home to many different religions over the centuries, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Islam. Each of these religions has influenced the Kannada language, and their influence can still be seen in the language today.
- The development of literature: Kannada has a rich literary tradition. The earliest known Kannada literary work is the Kavirajamarga, which was written in the 9th century CE. Since then, many great works of Kannada literature have been written, including the Ramayana, the Mahabharata, and the Bhagavad Gita. These works have all had a profound influence on the Kannada language, and their influence can still be seen in the language today.
- The influence of modernity: In the modern era, Kannada has been influenced by many factors, including the rise of nationalism, the spread of education, and the development of new technologies. These factors have all had a profound impact on the Kannada language, and their influence can still be seen in the language today.
Understanding the historical context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the historical events and movements that have influenced the language, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
3. Literary context
The literary context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. Kannada has a rich literary tradition, and the works of Kannada poets and writers have had a profound influence on the meaning of the language.
For example, the Kannada word "prema" means "love." However, the meaning of prema can vary depending on the context in which it is used. In a literary context, prema can refer to a deep and passionate love. However, in a more everyday context, prema can simply refer to a feeling of affection or fondness.
Another example is the Kannada word "mukha." Mukha means "face" in Kannada. However, in a literary context, mukha can also refer to the personality or character of a person. For example, a person with a "bright mukha" is someone who is cheerful and optimistic.
Understanding the literary context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the works of Kannada poets and writers, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.Conclusion
The literary context of Kannada is a complex and fascinating topic. By understanding the influence of Kannada poets and writers on the meaning of the language, interpreters can gain a deeper understanding of Kannada culture and literature.4. Grammatical Context
The grammatical context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. Kannada has a complex grammatical system, and the way that words are structured and combined can have a significant impact on their meaning.
For example, the Kannada word "" (mane) can mean "house" or "home." However, the meaning of mane can change depending on the grammatical context in which it is used. For example, if mane is used with the suffix "-" (-alli), it means "at home." If mane is used with the suffix "-" (-ge), it means "to home." Another example is the Kannada word "" (odu). Odu can mean "to read" or "to study." However, the meaning of odu can change depending on the grammatical context in which it is used. For example, if odu is used with the object "" (pustaka), it means "to read a book." If odu is used with the object "" (paatha), it means "to study a lesson." Understanding the grammatical context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the way that words are structured and combined, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
Conclusion
The grammatical context of Kannada is a complex and fascinating topic. By understanding the influence of grammar on the meaning of Kannada words and phrases, interpreters can gain a deeper understanding of Kannada language and culture.
5. Pragmatic context
The pragmatic context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. Kannada is a spoken language, and its meaning can be influenced by the context in which it is used. This includes the physical context, the social context, and the cultural context.
For example, the Kannada word "namaskara" can mean "hello" or "goodbye." However, the meaning of namaskara can change depending on the pragmatic context in which it is used. For example, if namaskara is said in a formal setting, it is likely to mean "hello." However, if namaskara is said in an informal setting, it is likely to mean "goodbye."
Another example is the Kannada word "anna." Anna means "brother" in Kannada. However, the meaning of anna can change depending on the pragmatic context in which it is used. For example, if anna is said to a younger brother, it is likely to mean "little brother." However, if anna is said to an older brother, it is likely to mean "big brother."
Understanding the pragmatic context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the context in which Kannada is used, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
Conclusion
The pragmatic context of Kannada is a complex and fascinating topic. By understanding the influence of context on the meaning of Kannada words and phrases, interpreters can gain a deeper understanding of Kannada language and culture.
6. Discourse context
Discourse context refers to the social and cultural context in which language is used. It includes the setting, the participants, and the purpose of the communication. Discourse context can have a significant impact on the meaning of words and phrases.
- The setting
The setting of a conversation can influence the meaning of what is said. For example, the same words might have different meanings if they are spoken in a formal setting, such as a business meeting, or in an informal setting, such as a conversation between friends. - The participants
The participants in a conversation can also influence the meaning of what is said. For example, the same words might have different meanings if they are spoken by a superior to a subordinate or by a friend to a friend. - The purpose of the communication
The purpose of the communication can also influence the meaning of what is said. For example, the same words might have different meanings if they are spoken to inform, to persuade, or to entertain.
Understanding the discourse context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the setting, the participants, and the purpose of the communication, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
7. Cognitive context
Cognitive context refers to the mental processes that are involved in understanding language. These processes include attention, memory, and inference. Cognitive context can have a significant impact on the meaning of words and phrases.
- Attention
Attention is the process of focusing on a particular stimulus. When we pay attention to something, we are more likely to remember it and to understand its meaning. For example, if we are listening to a conversation, we are more likely to understand what is being said if we are paying attention to the speaker. - Memory
Memory is the process of storing and retrieving information. When we remember something, we are able to access it later and to use it to understand new information. For example, if we have read a book, we are more likely to understand a new book on the same topic if we can remember what we read in the first book. - Inference
Inference is the process of drawing conclusions based on evidence. When we make an inference, we are using our knowledge and experience to fill in the gaps in our understanding. For example, if we see someone crying, we might infer that they are sad.
Understanding the cognitive context of Kannada is essential for interpreting meaning in the language. By considering the mental processes that are involved in understanding language, interpreters can ensure that they are accurately and effectively conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech.
Frequently Asked Questions about Interpreting Meaning in Kannada
This section provides answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about interpreting meaning in Kannada.
Question 1: What is the importance of cultural context when interpreting meaning in Kannada?
Answer: Cultural context is essential for interpreting meaning in Kannada because it provides insights into the values, beliefs, and traditions of the Kannada-speaking community. Understanding the cultural context helps interpreters to avoid misinterpretations and to convey the intended meaning of the original text or speech accurately.
Question 2: How does historical context influence the meaning of Kannada words and phrases?
Answer: Historical context provides information about the evolution of the Kannada language and the factors that have shaped its meaning over time. Understanding the historical context helps interpreters to appreciate the nuances of Kannada words and phrases and to convey their meaning accurately.
Question 3: What is the role of grammar in interpreting meaning in Kannada?
Answer: Grammar is essential for interpreting meaning in Kannada because it provides the rules for structuring words and phrases into meaningful sentences. Understanding Kannada grammar helps interpreters to identify the grammatical relationships between words and to convey the intended meaning of the original text or speech accurately.
Question 4: How does pragmatic context affect the meaning of Kannada words and phrases?
Answer: Pragmatic context refers to the context in which language is used, including the physical setting, the social situation, and the participants' intentions. Understanding the pragmatic context helps interpreters to determine the intended meaning of Kannada words and phrases and to convey their meaning accurately.
Question 5: What are the challenges of interpreting meaning in Kannada?
Answer: Interpreting meaning in Kannada can be challenging due to the language's complex grammar, rich vocabulary, and cultural nuances. Interpreters must have a deep understanding of the Kannada language and culture to convey the intended meaning of the original text or speech accurately.
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about interpreting meaning in Kannada. By understanding the cultural, historical, grammatical, pragmatic, and cognitive contexts of the language, interpreters can ensure that they are conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech accurately and effectively.
Summary: Interpreting meaning in Kannada requires a deep understanding of the language's cultural, historical, grammatical, pragmatic, and cognitive contexts. By considering these contexts, interpreters can ensure that they are conveying the intended meaning of the original text or speech accurately and effectively.
Transition: The next section provides a more detailed discussion of the challenges of interpreting meaning in Kannada.
Conclusion
Interpreting meaning in Kannada is a complex and challenging task that requires a deep understanding of the language's cultural, historical, grammatical, pragmatic, and cognitive contexts. Interpreters must be able to identify the nuances of Kannada words and phrases and to convey their intended meaning accurately.
The challenges of interpreting meaning in Kannada are numerous. The language's complex grammar, rich vocabulary, and cultural nuances can make it difficult for interpreters to convey the intended meaning of the original text or speech. However, by understanding the cultural, historical, grammatical, pragmatic, and cognitive contexts of the language, interpreters can overcome these challenges and ensure that they are conveying the intended meaning accurately and effectively.
Interpreting meaning in Kannada is an essential skill for anyone who works with the Kannada language. By understanding the challenges of interpreting meaning in Kannada, interpreters can ensure that they are providing accurate and effective interpretations.
You Might Also Like
Explore The Uncharted: Deep Dive Into Our Hot .LinkComprehensive Guide To Narrative Meaning In Kannada: Decoding Narratives For Deeper Understanding
Kerry Washington: Family Life With Her Husband And Children
The Ultimate Guide To The 1991 Chinese Zodiac: Your Personality Unveiled
Top-Rated Indian Ullu Web Series - Must-Watch For Entertainment
Article Recommendations