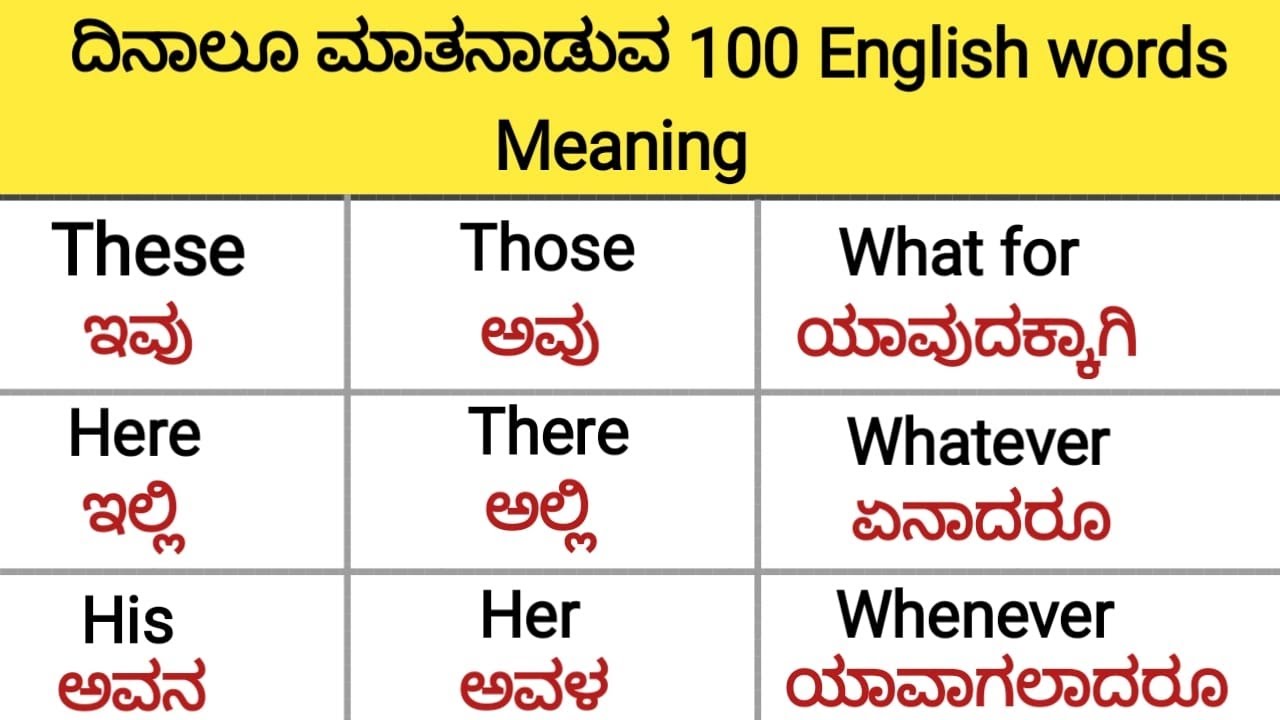
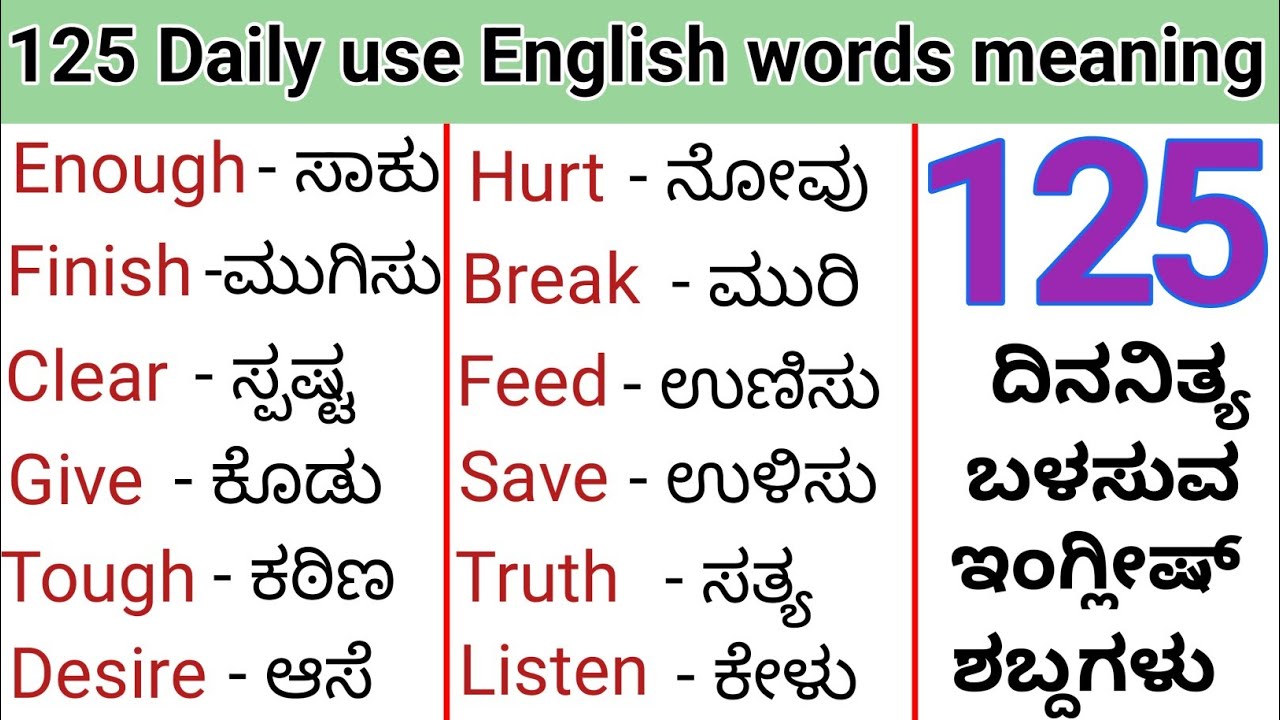
Kannada, the language of the land of Karnataka, holds a treasure trove of wisdom and culture. Its rich heritage and profound insights offer a deep understanding of life, emotions, and experiences. As one of the oldest Dravidian languages, Kannada is not just a means of communication but a repository of knowledge passed down through centuries. To truly grasp the insightful meaning in Kannada, one must delve into its literature, proverbs, and idiomatic expressions that reflect the ethos of its speakers.
The beauty of Kannada lies in its ability to convey complex ideas and emotions succinctly. Through its extensive vocabulary and nuanced expressions, Kannada provides a window into the soul of its people. The language is a reflection of the community's values, traditions, and beliefs, interwoven with stories of resilience, love, and wisdom. By exploring the insightful meaning in Kannada, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its cultural significance and the universal truths it embodies.
Understanding the insightful meaning in Kannada requires more than just linguistic knowledge; it demands an appreciation of the cultural context in which the language thrives. The idioms and sayings in Kannada are not mere strings of words but pearls of wisdom that offer guidance and perspective on life's journey. By engaging with Kannada's rich literary tradition and its oral storytelling heritage, one can uncover the layers of meaning that make this language truly remarkable.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Origins of Kannada
- Cultural Significance of Kannada
- Literary Treasures and Their Insights
- What Do Kannada Proverbs and Idioms Reveal?
- How is Kannada Relevant in Modern Times?
- Exploring the Diversity of Regional Dialects
- How Have Other Languages Influenced Kannada?
- The Role of Teaching in Preserving Kannada
- Kannada's Presence in Media and Entertainment
- Technological Advancements and Kannada's Future
- How is Kannada Embraced by the Global Community?
- Envisioning the Future of Kannada
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Understanding the Origins of Kannada
The Kannada language boasts a rich historical lineage, dating back to the 3rd century BCE. Its roots are deeply embedded in the Dravidian language family, sharing a close relationship with Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam. Kannada's evolution over the centuries has been influenced by various dynasties and empires that ruled the region, including the Chalukyas, Hoysalas, and Vijayanagara Empire. Each era contributed to the linguistic and cultural tapestry of Kannada, leaving an indelible mark on its structure and vocabulary.
From inscriptions on ancient temple walls to palm-leaf manuscripts, Kannada's journey is documented through a plethora of historical artifacts. The language has an extensive script known as the Kannada script, derived from the Kadamba script, which has evolved over time. The earliest known inscriptions in Kannada are the Halmidi inscription, dating back to 450 CE, which provides invaluable insights into the language's early form and usage.
As Kannada developed, it incorporated elements from Sanskrit, Prakrit, and Pali, enriching its lexicon and grammatical structure. This amalgamation of linguistic influences is evident in its literary works, which range from classical poetry and epics to philosophical treatises and folk songs. The language's adaptability and resilience have ensured its survival and relevance through centuries of change and upheaval.
Cultural Significance of Kannada
The cultural significance of Kannada extends beyond its role as a medium of communication. It is a vital part of Karnataka's identity, reflecting the customs, traditions, and ethos of its people. Kannada literature, music, dance, and art provide a glimpse into the region's rich cultural heritage, offering insights into the values and beliefs that have shaped its society.
Kannada literature, in particular, serves as a mirror to the region's cultural evolution. From the classical works of Pampa, Ranna, and Basava to contemporary authors like Kuvempu and U.R. Ananthamurthy, Kannada literature has explored themes of love, devotion, social justice, and humanism. These literary masterpieces not only capture the imagination of readers but also provide a deep understanding of the human condition and the complexities of life.
In addition to literature, Kannada plays a crucial role in preserving oral traditions and folklore. The language is the vehicle through which stories, legends, and myths are passed down through generations, keeping the region's cultural heritage alive. Festivals, rituals, and ceremonies celebrated in Karnataka are often steeped in Kannada language and traditions, further cementing its cultural significance.
Literary Treasures and Their Insights
Kannada's literary heritage is a treasure trove of insights and wisdom, offering a window into the minds and hearts of its people. The language has produced a wealth of literary works that span various genres, including poetry, prose, drama, and philosophical writings. These works are not only artistic expressions but also repositories of knowledge and introspection.
One of the most celebrated periods in Kannada literature is the Vachana movement of the 12th century, spearheaded by saints like Basava, Akka Mahadevi, and Allama Prabhu. The Vachanas, or free-verse poems, are profound reflections on spirituality, morality, and social reform. They challenge established norms and advocate for a more egalitarian and compassionate society, offering timeless insights into the human spirit.
Kannada epics like the Ramayana and Mahabharata, as retold by poets such as Pampa and Ranna, provide rich narratives that explore themes of duty, honor, and the eternal struggle between good and evil. These epic tales are imbued with moral and philosophical insights that resonate with readers across generations.
What Do Kannada Proverbs and Idioms Reveal?
Kannada proverbs and idioms are rich repositories of wisdom, offering pithy and poignant insights into the culture and values of its speakers. These expressions encapsulate complex ideas and life lessons in a few words, making them an integral part of everyday conversation.
Proverbs in Kannada often draw on imagery from nature, agriculture, and daily life, reflecting the agrarian roots of the region. They offer guidance on ethical behavior, interpersonal relationships, and the pursuit of happiness. For instance, the proverb "ಹಸಿವಾದಾಗ ಹುರಿದ ಹಿಟ್ಟು" (Hasivaadaaga hurida hittu) translates to "Roasted flour is tasty when hungry," emphasizing the importance of contentment and gratitude.
Idiomatic expressions in Kannada add color and depth to the language, allowing speakers to convey emotions and ideas with nuance and flair. They play a crucial role in storytelling and poetry, enhancing the impact of the narrative. Understanding these proverbs and idioms provides a deeper appreciation for the cultural and linguistic richness of Kannada.
How is Kannada Relevant in Modern Times?
In the modern world, Kannada continues to be a vibrant and dynamic language, adapting to the changing needs and aspirations of its speakers. It remains a vital medium of instruction, communication, and cultural expression in Karnataka and beyond.
Kannada's relevance in contemporary society is evident in its widespread use across various domains, including education, media, literature, and technology. The language is taught in schools and colleges, ensuring that future generations remain connected to their cultural and linguistic heritage. Kannada films, music, and television programs enjoy immense popularity, reaching audiences both within and outside India.
The digital age has further expanded the reach of Kannada, with the language making its mark on social media, websites, and mobile applications. Efforts to digitize Kannada literature and create online resources for language learners have made it more accessible to a global audience. These advancements have helped preserve and promote Kannada, ensuring its continued relevance in the modern era.
Exploring the Diversity of Regional Dialects
Kannada is not a monolithic language but a tapestry of diverse regional dialects, each with its unique characteristics and nuances. These dialects reflect the geographical, social, and cultural diversity of Karnataka, adding richness and variety to the language.
Some of the prominent regional dialects of Kannada include Mysore Kannada, Northern Kannada, Coastal Kannada, and Malnad Kannada. Each dialect has its distinct vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammatical features, influenced by the region's history, geography, and interactions with other language groups.
The existence of multiple dialects within Kannada is a testament to the language's adaptability and resilience. It allows speakers to express their identity and cultural heritage while remaining part of a larger linguistic community. Understanding these dialects provides valuable insights into the cultural and social fabric of Karnataka, highlighting the diversity and unity of its people.
How Have Other Languages Influenced Kannada?
Kannada, like many languages, has evolved through interactions with other linguistic and cultural traditions. Over the centuries, it has absorbed elements from languages such as Sanskrit, Prakrit, Pali, Telugu, Tamil, and Marathi, enriching its vocabulary and grammatical structure.
The influence of Sanskrit is particularly evident in Kannada's literary and religious texts, where many Sanskrit words and phrases have been assimilated. This linguistic exchange has enhanced the expressive and poetic capabilities of Kannada, allowing it to convey complex philosophical and spiritual ideas.
In more recent times, Kannada has also been influenced by English, particularly in technical and scientific domains. The incorporation of English terms and phrases reflects the language's ability to adapt to modern contexts and embrace new concepts and technologies. This ongoing exchange of linguistic elements ensures that Kannada remains a dynamic and evolving language, capable of meeting the needs of its speakers in a rapidly changing world.
The Role of Teaching in Preserving Kannada
Teaching plays a crucial role in preserving and promoting Kannada, ensuring that the language continues to thrive in future generations. Education in Kannada is a cornerstone of cultural transmission, providing students with the tools and knowledge to appreciate and engage with their linguistic heritage.
In Karnataka, Kannada is a compulsory subject in schools, where students learn to read, write, and speak the language. This formal education is supplemented by extracurricular activities, such as literary clubs, cultural festivals, and competitions, which encourage students to explore and celebrate Kannada's rich literary and artistic traditions.
Moreover, efforts to develop language resources, such as textbooks, dictionaries, and online platforms, have made learning Kannada more accessible and engaging. These initiatives are complemented by community-led efforts to promote Kannada through workshops, seminars, and cultural events, fostering a sense of pride and ownership among speakers.
Kannada's Presence in Media and Entertainment
Kannada's presence in media and entertainment is a testament to its enduring popularity and cultural significance. Kannada films, music, television programs, and literature continue to captivate audiences, both within and outside Karnataka, showcasing the language's versatility and appeal.
The Kannada film industry, known as Sandalwood, has produced numerous critically acclaimed and commercially successful films that have resonated with audiences worldwide. Kannada cinema explores a wide range of themes, from social issues and historical dramas to romance and comedy, reflecting the diversity and creativity of its filmmakers.
In addition to films, Kannada music and television programs have a broad following, with popular genres ranging from classical and folk music to contemporary pop and rock. Kannada literature, too, continues to thrive, with authors and poets producing works that explore contemporary issues and timeless themes, enriching the cultural landscape of the language.
Technological Advancements and Kannada's Future
Technological advancements have opened new avenues for the growth and promotion of Kannada, ensuring its continued relevance in the digital age. The proliferation of the internet, smartphones, and social media platforms has made Kannada more accessible to a global audience, allowing speakers to connect and share their experiences across borders.
Efforts to digitize Kannada literature, create online dictionaries, and develop language learning apps have made it easier for people to learn and engage with the language. These resources provide valuable support for language learners and enthusiasts, promoting Kannada's rich literary and cultural heritage.
Moreover, the use of Kannada in digital communication, such as social media posts, blogs, and websites, has helped preserve and promote the language in modern contexts. These technological advancements have ensured that Kannada remains a vibrant and dynamic language, capable of meeting the needs and aspirations of its speakers in an increasingly interconnected world.
How is Kannada Embraced by the Global Community?
The global community has increasingly embraced Kannada, recognizing its cultural and linguistic significance. Kannada-speaking diasporas in countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the Middle East have played a pivotal role in promoting the language and fostering cultural exchange.
Kannada associations and cultural organizations abroad organize events, workshops, and festivals that showcase the language's rich heritage, providing a platform for Kannada speakers to connect and celebrate their shared identity. These initiatives have helped raise awareness of Kannada's cultural contributions, fostering appreciation and understanding among diverse communities.
The global recognition of Kannada literature, films, and music has further enhanced its appeal, with translations and adaptations making it accessible to a wider audience. This growing interest in Kannada highlights its universal themes and insights, demonstrating the language's ability to transcend geographical and cultural boundaries.
Envisioning the Future of Kannada
The future of Kannada is bright, with continued efforts to preserve and promote the language ensuring its relevance for generations to come. As a living and evolving language, Kannada remains a vital part of Karnataka's cultural identity, reflecting the values, traditions, and aspirations of its people.
Efforts to promote Kannada in education, media, and technology will play a crucial role in shaping its future, ensuring that it remains a dynamic and adaptable language capable of meeting the needs of its speakers. The continued engagement of the global Kannada community will also be instrumental in fostering cultural exchange and appreciation, further enhancing the language's reach and impact.
As Kannada continues to evolve and adapt, it will remain a source of inspiration and insight, offering a window into the rich tapestry of human experience and the universal truths that connect us all. By embracing Kannada and its cultural heritage, we can ensure its continued vitality and relevance in an ever-changing world.
FAQs
What is the origin of the Kannada language?
Kannada is a Dravidian language with origins dating back to the 3rd century BCE. It has evolved over centuries, influenced by various dynasties, such as the Chalukyas and Vijayanagara Empire, and has absorbed elements from Sanskrit, Prakrit, and Pali.
How is Kannada literature significant?
Kannada literature is significant for its exploration of themes such as love, devotion, social justice, and humanism. It has produced renowned works, including classical poetry, epics, and modern novels, offering profound insights into the human condition and societal values.
What role do proverbs play in Kannada culture?
Kannada proverbs play a vital role in conveying cultural wisdom and values. They offer concise insights into ethical behavior, relationships, and life lessons, reflecting the agrarian roots and cultural heritage of the Kannada-speaking community.
How has technology impacted the Kannada language?
Technology has significantly impacted Kannada by making it more accessible globally. Digital resources, online platforms, and social media have facilitated language learning and communication, helping preserve and promote Kannada in modern contexts.
How is Kannada taught in schools?
In Karnataka, Kannada is a compulsory subject in schools. Students learn to read, write, and speak the language through formal education, supplemented by cultural activities and language resources, ensuring the preservation of linguistic heritage.
What is the global recognition of Kannada?
The global recognition of Kannada has grown, with diasporas promoting the language through cultural events and organizations. Kannada literature, films, and music have gained international acclaim, showcasing the language's cultural contributions and universal appeal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the insightful meaning in Kannada offers a profound understanding of the language's cultural and linguistic heritage. Through its rich literary tradition, proverbs, and idiomatic expressions, Kannada provides timeless insights into the human experience, reflecting the values and aspirations of its speakers. By exploring and preserving Kannada, we can ensure its continued relevance and vitality in a rapidly changing world, celebrating its unique contributions to the global cultural tapestry.
You Might Also Like
Sasha Luss Partner: The Dynamic Duo And Their JourneySkye Goddard: An In-Depth Profile Of An Influential Figure
Sean William Scott: A Star's Rise, Influence, And Impact On Hollywood
Wedding Of A Lifetime: The Event Of Chad Pergram
Gianna Michaels Instagram: An Insightful Journey Into Her Life And Career
Article Recommendations