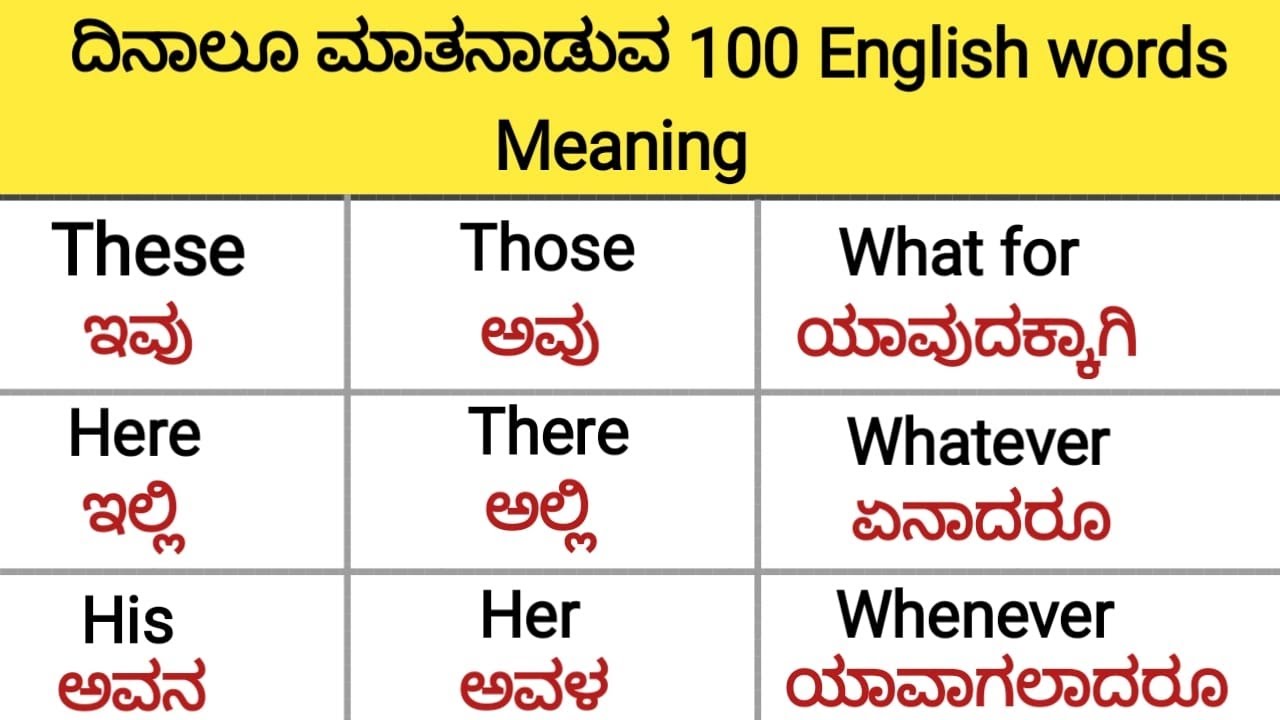
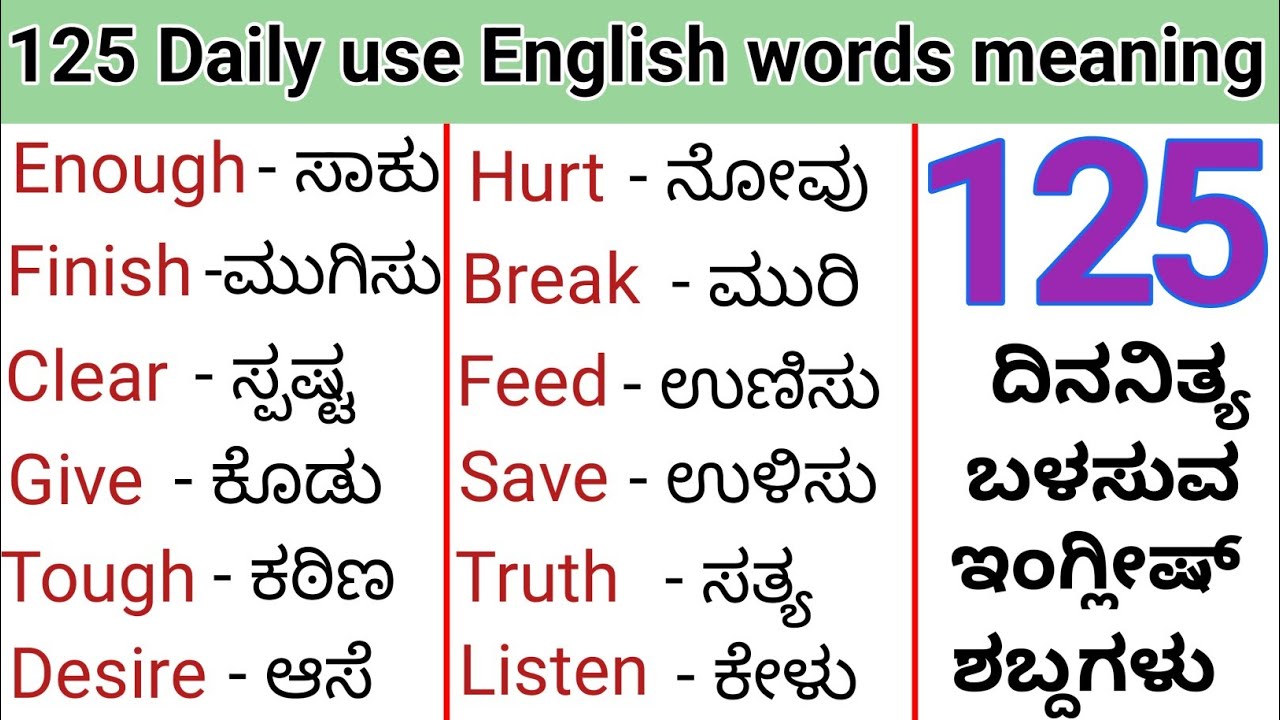
The Kannada language, rich in history and cultural significance, carries a wealth of meanings and interpretations. Understanding its nuances requires not just a translation of words but an appreciation for the cultural context and historical background that informs its usage. For those interested in diving deeper into the linguistic intricacies of Kannada, the phrase "interprets meaning in Kannada" serves as a gateway to exploring the language's profound depth. The exploration of Kannada interpretations goes beyond mere word-for-word translations. It involves delving into the cultural and linguistic layers that provide a more comprehensive understanding of the language. This understanding is not only beneficial for language enthusiasts but also for those interested in the cultural heritage of Karnataka, where Kannada is predominantly spoken.
Karnataka, with its vibrant history and cultural diversity, has Kannada as its official language. Interpreting meanings in Kannada involves an understanding of its grammar, syntax, and semantics, which are deeply intertwined with the region's cultural practices and traditions. This cultural lens is essential for grasping the subtleties and richness of the language, which is spoken by millions across the state and beyond.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of interpreting meanings in Kannada. From understanding basic phrases to exploring complex literary works, this article aims to provide insights into the linguistic elements that make Kannada a unique and fascinating language. Whether you're a student, a language enthusiast, or someone interested in the cultural aspects of Karnataka, this guide will offer valuable perspectives on how meanings are interpreted in Kannada.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Kannada: A Brief Overview
- What is the origin of the Kannada language?
- How is Kannada's grammatical structure unique?
- Why is cultural context important in Kannada?
- Exploring the literary significance of Kannada
- What are some common Kannada phrases?
- How has the Kannada language evolved over time?
- Challenges in interpreting Kannada meanings
- Modern usage of Kannada in digital media
- Effective methods for learning Kannada
- Are there effective translation tools for Kannada?
- Comparing Kannada with other Dravidian languages
- The cultural heritage preserved in Kannada
- The global influence of Kannada language
- FAQs
Understanding Kannada: A Brief Overview
Kannada is more than just a language; it is a reflection of the rich culture and history of Karnataka, India. Recognized as one of the classical languages of India, Kannada has a literary history that spans over a thousand years. The language is spoken by approximately 50 million people and is the official language of the state of Karnataka.
The earliest inscriptions in Kannada date back to the 6th century, and the language has evolved significantly over the centuries. Kannada literature has produced numerous works of poetry, prose, and drama, contributing to India's rich tapestry of linguistic diversity. Its script is visually distinctive and is derived from the Brahmi script, which also influenced several other Indian languages.
Kannada has a complex linguistic structure with three distinct dialects: Northern, Central, and Southern Kannada. Each dialect carries unique phonetic features and vocabulary that reflect the region's cultural nuances. Understanding these dialects is crucial for interpreting meanings in Kannada accurately.
What is the origin of the Kannada language?
The Kannada language has its roots in the Dravidian language family, which is one of the oldest language families in the world. The origins of Kannada can be traced back to the ancient Prakrit languages, which were prevalent in the Indian subcontinent around 2000 years ago. Over time, Kannada developed its distinct identity and characteristics, influenced by Sanskrit and other regional languages.
Historical records suggest that Kannada was used as a language of administration and literature during the reign of the Kadamba dynasty in the 4th century CE. The language further evolved under the patronage of various dynasties, including the Western Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, and the Hoysalas, each contributing to its literary and cultural richness.
Kannada's evolution is marked by the development of Old Kannada, Middle Kannada, and Modern Kannada, each stage representing significant linguistic and literary advancements. Today, Kannada stands as a testament to the rich cultural heritage of Karnataka and continues to thrive as a language of communication, education, and art.
How is Kannada's grammatical structure unique?
The grammatical structure of Kannada is both intricate and fascinating, reflecting the language's deep-rooted history and cultural context. Kannada grammar is characterized by its agglutinative nature, meaning that it forms words and expresses grammatical relationships through the addition of prefixes, suffixes, and infixes.
One of the unique aspects of Kannada grammar is its use of gender, number, and case systems. Nouns in Kannada are classified based on gender: masculine, feminine, and neuter. Additionally, Kannada employs a rich system of cases to indicate the grammatical role of nouns in a sentence, including nominative, accusative, dative, ablative, and instrumental cases.
Kannada verbs are conjugated based on tense, aspect, and mood, with distinct forms for various persons and numbers. The language also features a complex system of honorifics, which are used to convey respect and politeness in communication. These grammatical features make Kannada both a challenging and rewarding language to learn and interpret.
Why is cultural context important in Kannada?
The cultural context is paramount in understanding and interpreting meanings in Kannada, as the language is deeply intertwined with the traditions, customs, and values of Karnataka. Kannada expressions, idioms, and proverbs often draw from the region's rich cultural heritage, making it essential to consider the cultural backdrop when interpreting meanings.
For instance, many Kannada idioms are based on agricultural practices, festivals, and folklore, reflecting the agrarian lifestyle and cultural practices of the people. Understanding these cultural references is crucial for accurately interpreting the intended meaning and nuances of the language.
Moreover, Kannada literature and art are heavily influenced by Karnataka's historical and cultural developments. From the classical works of Pampa and Ranna to the modern writings of Kuvempu and U.R. Ananthamurthy, Kannada literature offers a window into the cultural evolution of the region. Interpreting these works requires an appreciation for the cultural context in which they were created.
Exploring the literary significance of Kannada
Kannada literature holds a prominent place in the Indian literary landscape, with a rich tradition that spans over a millennium. The literary history of Kannada is marked by a diverse range of works, including poetry, prose, drama, and philosophical treatises, reflecting the region's cultural and intellectual vitality.
One of the earliest and most celebrated works in Kannada literature is the "Kavirajamarga," a treatise on poetics and grammar written in the 9th century by King Amoghavarsha. This work laid the foundation for the development of classical Kannada literature and inspired subsequent generations of writers and poets.
Kannada literature has produced numerous distinguished writers and poets, including Pampa, Ranna, Basavanna, and Akka Mahadevi. These literary figures have made significant contributions to the fields of poetry, philosophy, and social reform, using Kannada as a medium to express their ideas and vision.
In modern times, Kannada literature has continued to flourish, with writers like Kuvempu, U.R. Ananthamurthy, and Girish Karnad gaining national and international recognition. Their works address contemporary social, political, and cultural issues, reflecting the evolving realities of Karnataka and beyond.
What are some common Kannada phrases?
Learning common Kannada phrases is an excellent way to build a foundation for understanding and communicating in the language. Here are some commonly used phrases in Kannada:
- Namaskara (ನಮಸ್ಕಾರ) - Hello
- Hegiddira? (ಹೇಗಿದ್ದೀರ?) - How are you?
- Dhanyavaadagalu (ಧನ್ಯವಾದಗಳು) - Thank you
- Dayavittu (ದಯವಿಟ್ಟು) - Please
- Naanu Kannada kalithu (ನಾನು ಕನ್ನಡ ಕಲಿತು) - I am learning Kannada
- Elli ide (ಎಲ್ಲಿ ಇದೆ) - Where is it?
These phrases provide a starting point for engaging with Kannada speakers and understanding the language's basic structure and vocabulary. As you become more familiar with the language, you can expand your vocabulary and explore more complex expressions and idioms.
How has the Kannada language evolved over time?
The evolution of the Kannada language is a testament to its resilience and adaptability in the face of historical and cultural changes. Kannada has undergone significant transformations over the centuries, influenced by various dynasties, linguistic developments, and cultural exchanges.
Old Kannada, which emerged around the 6th century CE, laid the foundation for the language's development. During this period, Kannada was used primarily in inscriptions and literary works, with a focus on poetry and religious texts. The language evolved into Middle Kannada between the 12th and 18th centuries, marked by the influence of Sanskrit and the emergence of new literary forms.
Modern Kannada, which developed from the 18th century onwards, reflects the language's continued evolution and adaptation to contemporary realities. Today, Kannada is spoken by millions of people in Karnataka and beyond, serving as a medium of communication, education, and cultural expression.
Challenges in interpreting Kannada meanings
Interpreting meanings in Kannada presents several challenges, particularly for non-native speakers and those unfamiliar with the language's cultural context. Some of the key challenges include:
- Dialectal Variations: Kannada has multiple dialects, each with unique phonetic features and vocabulary. Understanding these dialects is crucial for accurate interpretation.
- Idiomatic Expressions: Kannada is rich in idioms and proverbs that draw from cultural and historical references. Interpreting these expressions requires an understanding of their cultural significance.
- Complex Grammar: Kannada's agglutinative grammar and case system can be challenging for learners to grasp, requiring a deep understanding of linguistic rules.
- Literary References: Kannada literature often includes references to historical and cultural events, requiring contextual knowledge for accurate interpretation.
Despite these challenges, learning Kannada and interpreting its meanings can be a rewarding experience, offering insights into the language's rich cultural and historical heritage.
Modern usage of Kannada in digital media
In the digital age, Kannada has found new avenues for expression and communication, with digital media playing a significant role in its modern usage. Social media platforms, websites, and mobile applications have made it easier for Kannada speakers to connect, share, and access information in their language.
Kannada content creators have embraced digital platforms to produce a wide range of content, including news, entertainment, education, and cultural programs. This has led to the proliferation of Kannada blogs, podcasts, YouTube channels, and social media pages, catering to diverse interests and audiences.
The rise of digital media has also facilitated the development of online tools and resources for learning Kannada, making it more accessible to learners worldwide. Language learning apps, online courses, and digital dictionaries have made it easier for individuals to learn Kannada and engage with its rich linguistic and cultural heritage.
Effective methods for learning Kannada
Learning Kannada can be a fulfilling and enriching experience, offering insights into the language's cultural and historical significance. Here are some effective methods for learning Kannada:
- Language Classes: Enrolling in Kannada language classes or courses, either in-person or online, provides structured learning and guidance from experienced instructors.
- Language Exchange: Engaging in language exchange programs with native Kannada speakers allows for practical language practice and cultural exchange.
- Online Resources: Utilizing online resources such as language learning apps, websites, and digital dictionaries can aid in vocabulary building and language comprehension.
- Immersive Experience: Immersing oneself in Kannada-speaking environments, such as visiting Karnataka or participating in cultural events, enhances language learning through real-world interaction.
- Consistent Practice: Regular practice and exposure to Kannada, through reading, writing, listening, and speaking, are essential for language acquisition and proficiency.
With dedication and the right resources, learners can gain proficiency in Kannada and unlock the linguistic and cultural treasures of the language.
Are there effective translation tools for Kannada?
With the advancement of technology, several translation tools have emerged to assist users in translating Kannada to other languages and vice versa. Some of the most effective translation tools for Kannada include:
- Google Translate: Google Translate supports Kannada and offers translation services for words, phrases, and sentences. It also provides a text-to-speech feature for pronunciation assistance.
- Microsoft Translator: Microsoft Translator offers Kannada translation services and supports text, speech, and image translation, making it a versatile tool for language learners.
- Kannada-English Dictionary Apps: Several mobile apps offer Kannada-English dictionaries, providing translations, definitions, and examples for learners and users.
While these tools can be helpful for basic translations, it is important to note that they may not always capture the cultural nuances and idiomatic expressions of Kannada. For accurate and contextually appropriate translations, consulting native speakers or professional translators is recommended.
Comparing Kannada with other Dravidian languages
Kannada is one of the major Dravidian languages, sharing linguistic roots and characteristics with other Dravidian languages such as Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam. While these languages have distinct identities, they also exhibit similarities that reflect their common ancestry.
Some of the similarities between Kannada and other Dravidian languages include:
- Phonetic Features: Dravidian languages share common phonetic features, including the use of retroflex consonants and a similar vowel system.
- Grammar: The agglutinative nature of Dravidian languages is a shared characteristic, with similar verb conjugation patterns and case systems.
- Vocabulary: Many Dravidian languages share cognates and loanwords, reflecting historical interactions and cultural exchanges.
Despite these similarities, each Dravidian language has developed its unique literary traditions, dialects, and linguistic features. Comparing Kannada with other Dravidian languages offers insights into the linguistic diversity and cultural richness of the Dravidian language family.
The cultural heritage preserved in Kannada
Kannada is not just a language; it is a repository of the cultural heritage and traditions of Karnataka. Through its literature, art, music, and folklore, Kannada preserves the historical and cultural legacy of the region, offering insights into the values, beliefs, and practices of its people.
Kannada literature is replete with works that reflect the region's cultural ethos, from the classical poetry of Pampa and Ranna to the modern writings of Kuvempu and U.R. Ananthamurthy. These literary works explore themes of love, devotion, social justice, and human values, providing a window into the cultural and intellectual landscape of Karnataka.
Kannada art and music, including classical dance forms like Bharatanatyam and folk traditions like Yakshagana, are integral to the region's cultural heritage. These art forms use Kannada as a medium of expression, preserving the language and its cultural significance for future generations.
The global influence of Kannada language
While Kannada is primarily spoken in Karnataka, its influence extends beyond regional borders, reaching a global audience through literature, cinema, and digital media. The global Kannada diaspora has played a significant role in promoting the language and culture on the international stage.
Kannada literature has gained international recognition, with translations of works by writers like U.R. Ananthamurthy and Girish Karnad reaching global audiences. Kannada cinema, known for its innovative storytelling and artistic excellence, has also garnered attention and acclaim worldwide.
The rise of digital media has further expanded the reach of Kannada, with online platforms enabling Kannada speakers to connect and share their culture and language with a global audience. This global influence reflects the dynamic and evolving nature of Kannada as a language of communication and cultural expression.
FAQs
1. What is the official status of Kannada?
Kannada is the official language of the Indian state of Karnataka and is recognized as one of the classical languages of India.
2. How many people speak Kannada?
Kannada is spoken by approximately 50 million people, primarily in the state of Karnataka, India.
3. What are some popular Kannada literature works?
Some popular Kannada literary works include "Kavirajamarga" by King Amoghavarsha, the poetry of Pampa and Ranna, and modern works by Kuvempu and U.R. Ananthamurthy.
4. Are there Kannada language learning resources available online?
Yes, there are several online resources for learning Kannada, including language learning apps, websites, and digital dictionaries.
5. How does Kannada's grammatical structure differ from English?
Kannada's grammatical structure is agglutinative, with a rich system of cases, gender, and honorifics, differing significantly from the syntax and grammar of English.
6. What is the significance of cultural context in interpreting Kannada?
Cultural context is crucial in interpreting Kannada, as the language is deeply intertwined with the traditions, customs, and values of Karnataka.
The exploration of "interprets meaning in Kannada" offers a fascinating journey into the language's linguistic, cultural, and historical dimensions. Whether you're a language learner or a cultural enthusiast, understanding Kannada's meanings provides valuable insights into its rich heritage and contemporary relevance.
For more information on the Kannada language and its cultural significance, visit Wikipedia: Kannada.
You Might Also Like
Auli'i Cravalho Husband: Everything You Need To KnowPastries Meaning In Kannada: A Delicious Exploration
Role Meaning In Kannada: Insights And Implications
Secrets Of Marlene Favela: Her Life, Career, And Personal Journey
Harnessing The Impact Of Deliberate Intent: A Deep Dive Into Purposeful Action
Article Recommendations