Ethnicity, a concept that has shaped societies and cultures across the globe, holds a significant place in the diverse tapestry of human existence. In the vibrant state of Karnataka, India, ethnicity manifests itself in a rich mosaic of communities, each with its unique traditions, languages, and customs.
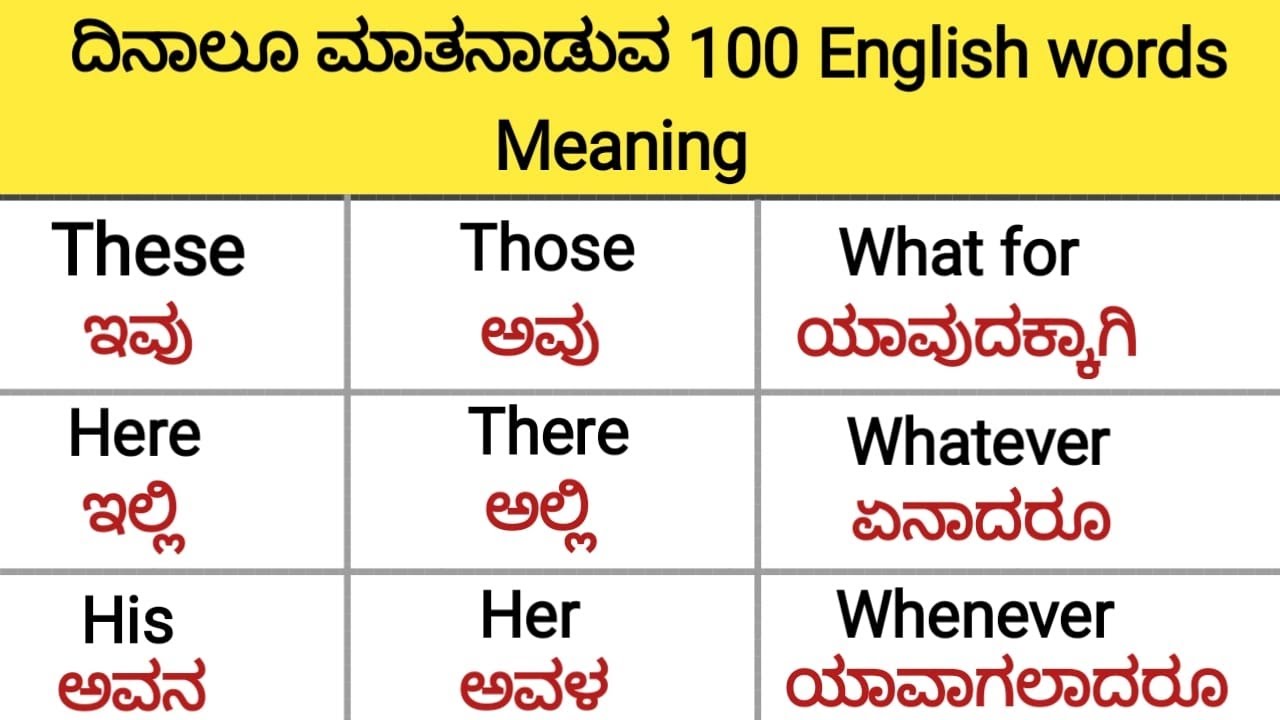
The term "ethnicity" in Kannada, the official language of Karnataka, is "jati." It refers to the shared cultural and social characteristics that define a particular group of people, including their ancestry, language, religion, and customs. Ethnicity serves as a powerful force in shaping individuals' identities, influencing their sense of belonging, and fostering a sense of community.
Karnataka's ethnic diversity is a testament to the state's long and fascinating history. Over the centuries, Karnataka has been home to various empires and kingdoms, each leaving its imprint on the region's cultural landscape. From the Chalukyas and Rashtrakutas to the Hoysalas and Vijayanagara Empire, each dynasty contributed to the rich tapestry of ethnicities that make up modern-day Karnataka.
Today, Karnataka is a vibrant hub of diverse ethnic communities. The state is home to several linguistic groups, including Kannada, Tulu, Konkani, and Kodava. Religious diversity is also a defining feature of Karnataka, with Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Jainism being widely practiced. These diverse ethnicities coexist harmoniously, contributing to the state's cultural richness and social fabric.
Understanding ethnicity and its significance is crucial for fostering inclusivity and social cohesion in Karnataka. By embracing the state's ethnic diversity, we can celebrate the unique contributions of each community and work towards building a truly equitable and harmonious society.
ethnicity meaning in kannada
Understanding the meaning of ethnicity in Kannada, referred to as "jati," is crucial for navigating the diverse cultural landscape of Karnataka, India. Ethnicity encompasses several key aspects that shape the identities and experiences of individuals within the state.
- Language: Kannada, Tulu, Konkani, Kodava
- Religion: Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Jainism
- Culture: Traditional festivals, music, dance, cuisine
- History: Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Hoysalas, Vijayanagara Empire
- Society: Caste system, joint families, rural-urban divide
- Identity: Sense of belonging, community ties
- Diversity: Harmony, coexistence, inclusivity
These aspects are interconnected and influence each other, creating a rich tapestry of ethnicities in Karnataka. Language, religion, and culture are closely intertwined, shaping the daily lives and practices of individuals. Historical influences have left a lasting impact on the ethnic makeup of the state, contributing to the diversity of communities. Social structures, such as the caste system and family dynamics, play a role in shaping ethnic identities. Ultimately, ethnicity in Karnataka is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a sense of belonging, cultural heritage, and shared experiences, fostering a vibrant and diverse society.
1. Language
Language plays a pivotal role in shaping ethnicity, serving as a primary marker of cultural identity and a means of communication within a community. In the context of "ethnicity meaning in kannada," the languages Kannada, Tulu, Konkani, and Kodava hold significant importance.
- Identity and Belonging:
Language is a powerful force in shaping individuals' sense of identity and belonging. Speaking Kannada, Tulu, Konkani, or Kodava connects individuals to a shared cultural heritage, fostering a sense of community and belonging among its speakers.
- Cultural Expression and Transmission:
Language serves as a medium for cultural expression and transmission. Through these languages, communities pass down traditions, stories, and knowledge from one generation to another, preserving their unique cultural heritage.
- Socialization and Communication:
Language facilitates socialization and communication within a community. By sharing a common language, individuals can effectively interact, build relationships, and participate in social activities, strengthening the bonds that unite the community.
- Historical and Geographic Influences:
The distribution of languages in Karnataka is influenced by historical and geographic factors. Kannada, the official language of the state, is widely spoken across the region. Tulu is predominantly spoken in the coastal districts, while Konkani is prevalent in the western coastal areas. Kodava is primarily spoken by the Kodava community in the Kodagu region.
In conclusion, the languages Kannada, Tulu, Konkani, and Kodava are integral to understanding "ethnicity meaning in kannada." They embody the cultural identity, heritage, and social dynamics of the diverse communities in Karnataka, contributing to the rich tapestry of ethnicities that define the state.
2. Religion
Religion plays a significant role in shaping ethnicity, influencing cultural practices, beliefs, and values within a community. In the context of "ethnicity meaning in kannada," Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Jainism are four major religions that have influenced the cultural landscape of Karnataka, India.
- Identity and Belonging:
Religion serves as a primary marker of identity and belonging, fostering a sense of community and shared values among its followers. In Karnataka, individuals identify with their respective religions, which shapes their cultural practices, festivals, and social interactions.
- Cultural Practices and Beliefs:
Religion influences cultural practices and beliefs within a community. Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Jainism have distinct rituals, festivals, and dietary practices that shape the daily lives of their followers in Karnataka.
- Historical and Geographic Influences:
The distribution of religions in Karnataka is influenced by historical and geographic factors. Hinduism is the majority religion, followed by Islam, Christianity, and Jainism. The presence of these religions reflects the state's rich history and cultural interactions.
- Social and Cultural Diversity:
Religion contributes to the social and cultural diversity of Karnataka. Different religious communities have their unique traditions, customs, and festivals, which enrich the cultural tapestry of the state. This diversity fosters interfaith dialogue and promotes cultural understanding.
In conclusion, the religions Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Jainism are integral to understanding "ethnicity meaning in kannada." They shape the cultural identity, beliefs, and practices of diverse communities in Karnataka, contributing to the rich and vibrant ethnic landscape of the state.
3. Culture
Culture, encompassing traditional festivals, music, dance, and cuisine, plays a vital role in defining ethnicity and shaping community identity. In the context of "ethnicity meaning in kannada," culture serves as a powerful force that unifies and distinguishes various ethnic groups in Karnataka, India.
Traditional festivals are central to cultural expression and identity. Each community celebrates unique festivals that commemorate historical events, religious beliefs, or seasonal changes. These festivals bring people together, fostering a sense of belonging and strengthening community bonds. For example, the harvest festival of Sankranti, celebrated across Karnataka, is a joyous occasion marked by traditional dances, music, and feasts.
Music and dance are integral to cultural expression and storytelling. Different ethnic groups in Karnataka have their distinct musical styles and dance forms. These art forms reflect the community's history, traditions, and beliefs. For instance, the vibrant folk music of North Karnataka, influenced by Hindustani classical music, showcases the region's cultural heritage.
Cuisine is a defining aspect of culture, offering a glimpse into the culinary traditions and food habits of a community. Each ethnic group in Karnataka has its unique cuisine, influenced by local ingredients, cooking techniques, and cultural preferences. For example, the spicy and flavorful cuisine of the Udupi region, known for its vegetarian dishes, is a testament to the region's cultural identity.
Understanding the connection between culture and ethnicity is crucial for preserving and promoting the diverse cultural heritage of Karnataka. By appreciating the traditional festivals, music, dance, and cuisine of different ethnic groups, we can foster inclusivity, celebrate diversity, and strengthen the bonds that unite the communities of Karnataka.
4. History
The rich history of Karnataka, marked by the rise and fall of several empires, has played a significant role in shaping the cultural landscape and ethnicity of the state. The Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Hoysalas, and Vijayanagara Empire left an indelible mark on the region, contributing to the diverse ethnicities that exist in Karnataka today.
- Political and Cultural Patronage:
These empires were patrons of art, architecture, and literature, which flourished under their rule. The construction of magnificent temples, forts, and monuments showcased the cultural achievements of each dynasty and influenced the artistic traditions of the region. For example, the Chalukyan architecture of the Aihole and Pattadakal temples reflects the empire's grandeur and artistic prowess.
- Migration and Settlement:
The rise and fall of empires led to population movements and migrations. People from different regions settled in Karnataka, bringing their cultural practices and beliefs. These migrations contributed to the ethnic diversity of the state, as new communities emerged and interacted with existing ones.
- Social and Economic Changes:
The empires implemented administrative systems, land grants, and economic policies that shaped social and economic structures. These changes influenced the livelihoods, occupations, and social hierarchies within different communities, contributing to the formation of ethnic identities.
- Cultural Exchange and Assimilation:
The empires fostered cultural exchange between different regions under their rule. This led to the assimilation of cultural practices, beliefs, and artistic styles. For example, the Hoysala period witnessed the influence of both Dravidian and North Indian architectural styles in temple construction.
Understanding the connection between "History: Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Hoysalas, Vijayanagara Empire" and "ethnicity meaning in kannada" provides insights into the historical roots of cultural diversity in Karnataka. The empires' political, cultural, social, and economic influences have shaped the ethnic identities and traditions that continue to define the state's rich cultural heritage.
5. Society
The intricate social fabric of Karnataka, woven with the threads of caste system, joint families, and rural-urban divide, is inextricably linked to the concept of "ethnicity meaning in kannada." These societal structures have shaped cultural identities, community dynamics, and social interactions within the state.
- Caste System:
The caste system, a hierarchical social structure based on birth, has historically influenced ethnic identities in Karnataka. Different castes have distinct cultural practices, occupations, and social norms, contributing to the diversity of ethnic groups within the state.
- Joint Families:
The tradition of joint families, where multiple generations live under one roof, fosters close family ties and a sense of extended community. This social structure reinforces ethnic identities and cultural values within families, shaping the upbringing and socialization of individuals.
- Rural-Urban Divide:
The rural-urban divide in Karnataka has led to disparities in access to resources, education, and employment opportunities. This divide can influence ethnic identities, as individuals from different geographic regions may have distinct cultural practices, economic backgrounds, and social challenges.
Understanding the connection between "Society: Caste system, joint families, rural-urban divide" and "ethnicity meaning in kannada" provides a deeper comprehension of the social and cultural dynamics that shape the diverse ethnicities of Karnataka. These societal structures have played a significant role in the formation of cultural identities, community interactions, and the preservation of cultural traditions within the state.
6. Identity
In the context of "ethnicity meaning in kannada," the facets of identity encompass a sense of belonging and community ties. These facets play a crucial role in shaping ethnic identities and fostering a shared sense of community among individuals.
- Belonging and Shared Heritage:
A sense of belonging is a fundamental aspect of ethnicity. Individuals identify with their ethnic group based on shared cultural heritage, language, traditions, and history. This sense of belonging fosters a deep connection to the community and a shared understanding of cultural norms and values.
- Community Ties and Networks:
Community ties are vital for maintaining and strengthening ethnic identities. Individuals within an ethnic group often form close relationships, establish networks, and participate in community activities. These ties provide support, a sense of security, and opportunities for cultural exchange, reinforcing ethnic bonds.
- Cultural Practices and Expressions:
Cultural practices and expressions are closely linked to ethnic identity. Participating in traditional festivals, performing folk dances, and practicing cultural rituals strengthens a sense of community and distinguishes one ethnic group from another. These practices provide a platform for cultural preservation and transmission.
- Language and Communication:
Language serves as a powerful marker of ethnic identity. Speaking a common language facilitates communication, fosters a sense of unity, and preserves cultural traditions. Language use within an ethnic community reinforces its distinct identity and contributes to intergenerational transmission of cultural knowledge.
In conclusion, the facets of "Identity: Sense of belonging, community ties" are integral to understanding "ethnicity meaning in kannada." They shape the cultural landscape of Karnataka, fostering a sense of shared heritage, community, and cultural practices that distinguish and unite various ethnic groups within the state.
7. Diversity
Within the context of "ethnicity meaning in kannada," the concept of diversity encompasses harmony, coexistence, and inclusivity, playing a vital role in fostering a cohesive and vibrant society.
- Harmony and Mutual Respect:
Despite the diverse ethnicities in Karnataka, there exists a remarkable sense of harmony and mutual respect among different communities. Individuals recognize and appreciate the unique customs, traditions, and beliefs of others, fostering a peaceful and tolerant environment.
- Coexistence and Shared Spaces:
Ethnic communities in Karnataka coexist peacefully, sharing public spaces, marketplaces, and civic amenities. This coexistence allows for cultural exchange, intermingling, and a sense of shared belonging, breaking down barriers and promoting unity.
- Inclusivity and Equal Opportunities:
Karnataka strives for inclusivity, ensuring equal opportunities for individuals from all ethnic backgrounds. Government policies, educational institutions, and workplaces actively promote diversity and inclusion, allowing all members of society to participate and contribute to the state's progress.
In conclusion, the facets of "Diversity: Harmony, coexistence, inclusivity" are crucial to the understanding of "ethnicity meaning in kannada." These principles underpin the harmonious relationships, shared spaces, and equal opportunities that characterize the diverse ethnic landscape of Karnataka, contributing to a cohesive and vibrant society.
FAQs on "ethnicity meaning in kannada"
This section addresses frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What is the significance of ethnicity in Karnataka?
Answer: Ethnicity plays a vital role in shaping the cultural identity, traditions, and social dynamics of Karnataka. It encompasses shared language, religion, customs, and history, contributing to the diversity and richness of the state's cultural heritage.
Question 2: How does ethnicity impact daily life in Karnataka?
Answer: Ethnicity influences various aspects of daily life, including language use, religious practices, festivals, cuisine, and social interactions. It shapes individuals' sense of belonging, community ties, and cultural expression.
Question 3: What are the major ethnic groups in Karnataka?
Answer: Karnataka is home to diverse ethnic groups, including Kannadigas, Tuluvas, Konkanis, Kodavas, and several other smaller communities. Each group has its unique cultural practices, traditions, and language, contributing to the state's rich tapestry of ethnicities.
Question 4: How does the government of Karnataka promote ethnic harmony?
Answer: The government recognizes the importance of ethnic diversity and actively promotes harmony through policies that encourage inclusivity, equal opportunities, and respect for different cultures. It supports cultural events, festivals, and educational initiatives that celebrate and preserve the unique heritage of each ethnic group.
Question 5: What is the importance of preserving ethnic diversity in Karnataka?
Answer: Preserving ethnic diversity is crucial for maintaining the cultural richness and heritage of Karnataka. It fosters a sense of belonging, community, and pride among individuals, while also promoting mutual understanding, respect, and social cohesion.
In conclusion, understanding "ethnicity meaning in kannada" provides insights into the diverse cultural landscape of Karnataka and its impact on various aspects of life. Preserving and celebrating ethnic diversity is essential for maintaining the state's rich cultural heritage and fostering a harmonious society.
Proceed to the next section to explore additional aspects related to "ethnicity meaning in kannada."
Conclusion
The exploration of "ethnicity meaning in kannada" has shed light on the multifaceted nature of cultural identity and its profound influence on various aspects of life in Karnataka. Ethnicity, encompassing shared language, religion, customs, and history, serves as a cornerstone of cultural heritage and shapes the unique tapestry of communities within the state.
Karnataka's rich history, diverse geography, and harmonious coexistence of ethnic groups have contributed to the vibrant cultural landscape we witness today. Understanding and embracing ethnic diversity is not only vital for preserving cultural heritage but also for fostering inclusivity, mutual respect, and social cohesion. It is through the recognition and celebration of our shared cultural wealth that we can truly build a harmonious and progressive society.
You Might Also Like
Meaning Of Dreams In Telugu | Discover The Hidden SymbolismCary Grant's Father: Uncovering The Patriarch Of A Hollywood Legend
Full Insight: What Does Existed Mean In Telugu?
Movies: Watch The Latest Movies & TV Shows Online On Movierulz.7
The Ultimate Guide To Reflection Meaning In Kannada
Article Recommendations