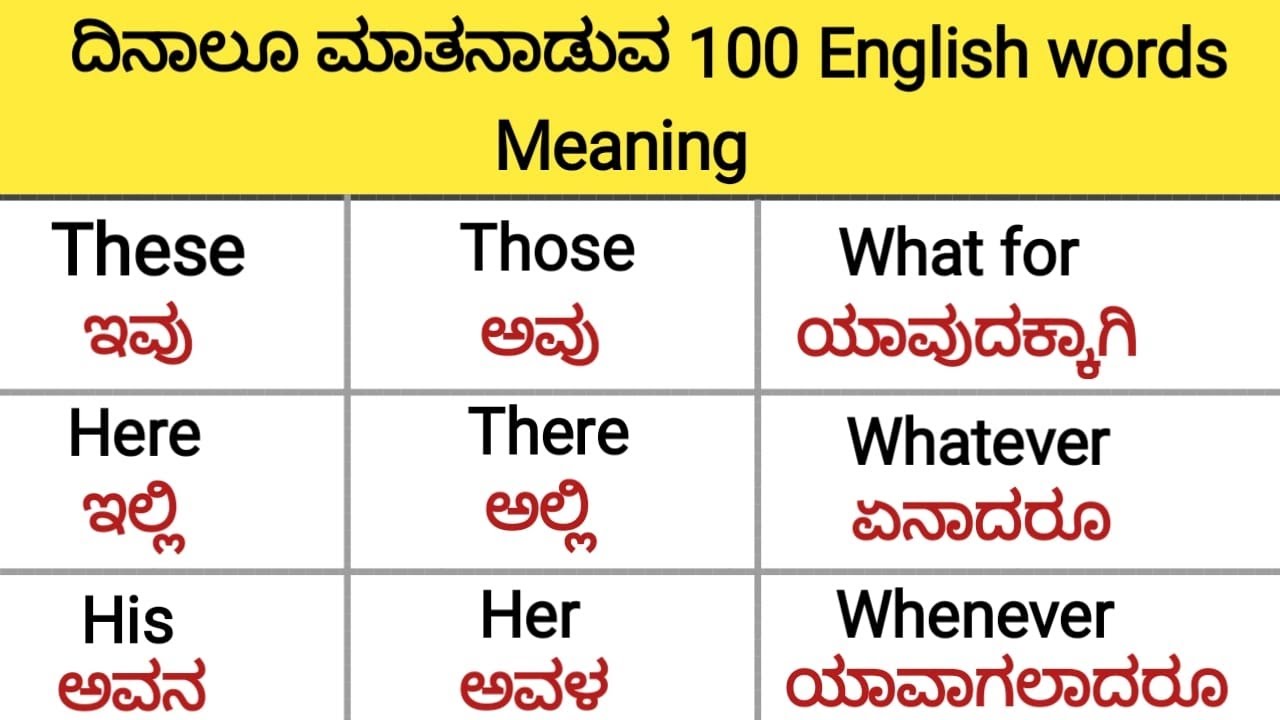
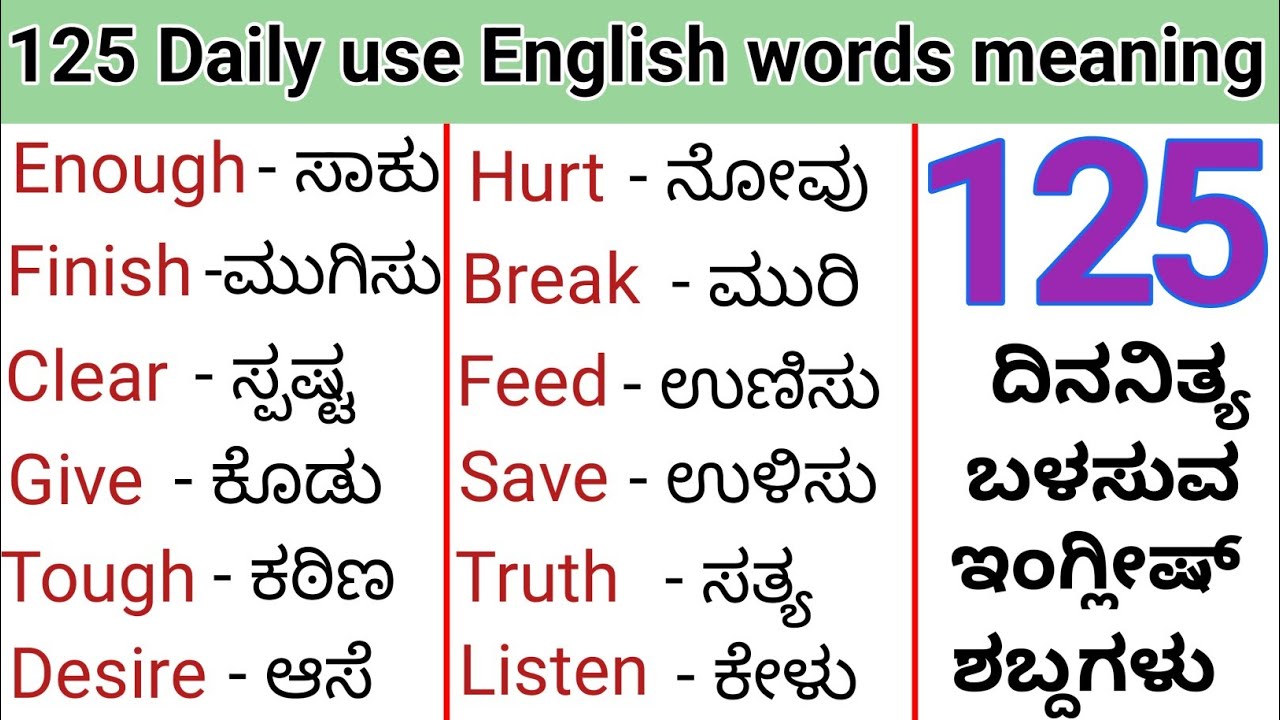
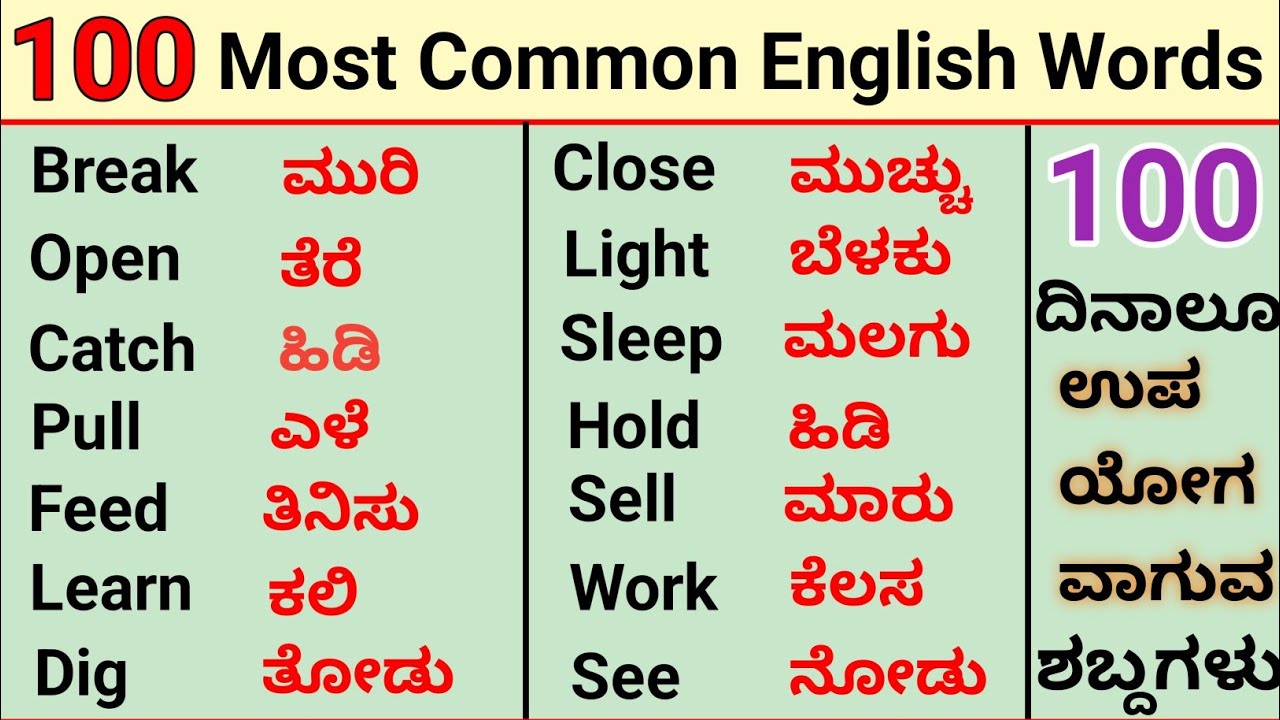
Reflection, in the context of language translation, refers to the process of expressing the meaning of a word or phrase in another language. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately.
In Kannada, the word for "reflection" is "" (parivartane). This term encompasses the idea of transformation or change, implying that the meaning of a word or phrase in one language may undergo a subtle shift when translated into another. Translators must therefore possess a deep understanding of both languages to capture the essence of the original text while ensuring its comprehensibility in the target language.
Reflection is a crucial aspect of effective translation, as it allows for the preservation of the intended meaning and tone of the source material. By carefully considering the cultural and linguistic context, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the message to the target audience.
Reflection Meaning in Kannada
Reflection, in the context of language translation, refers to the process of expressing the meaning of a word or phrase in another language. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately.
- Transformation
- Change
- Meaning Shift
- Cultural Context
- Linguistic Nuances
- Accuracy
- Comprehensibility
- Preservation of Meaning
These key aspects highlight the importance of reflection in translation. By carefully considering each of these factors, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the message to the target audience. For example, the cultural context of a word or phrase can significantly impact its meaning. A translator must be aware of these cultural differences to avoid misinterpretation or offense.
1. Transformation
In the context of language translation, transformation plays a pivotal role in reflection, the process of expressing the meaning of a word or phrase in another language. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately. Transformation, in this sense, refers to the subtle shifts in meaning that may occur when a word or phrase is translated from one language to another.
For instance, the English word "reflection" can be translated to "" (parivartane) in Kannada. While both words share the general idea of change or transformation, the Kannada term carries a slightly different connotation. In Kannada, "parivartane" often implies a more profound or fundamental change, a transformation that affects the very nature or essence of something. This subtle difference in meaning highlights the importance of considering the cultural and linguistic context when translating from one language to another.
Understanding the connection between transformation and reflection meaning in Kannada is crucial for effective translation. By carefully considering the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the message to the target audience.
2. Change
The concept of "change" is closely intertwined with "reflection meaning in Kannada," as it encapsulates the transformative nature of the translation process. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately. Change, in this context, refers to the subtle shifts in meaning that may occur when a word or phrase is translated from one language to another.
- Cultural Context
Cultural context plays a significant role in shaping the meaning of words and phrases. When translating from English to Kannada, translators must be aware of the cultural differences between the two languages to avoid misinterpretation or offense. For example, the English word "reflection" may have different connotations in different cultures. In some cultures, it may refer to a thoughtful consideration of an idea or experience, while in other cultures, it may refer to a physical reflection or image. Translators must carefully consider the cultural context of the source text to ensure that the translation accurately conveys the intended meaning.
- Linguistic Nuances
Linguistic nuances also contribute to the transformative nature of reflection meaning in Kannada. Different languages have their own unique grammatical structures, idioms, and expressions. Translators must be familiar with the linguistic nuances of both the source and target languages to ensure that the translation is both accurate and natural-sounding. For example, the English word "reflection" can be translated to "" (parivartane) in Kannada. However, the Kannada word carries a slightly different connotation, implying a more profound or fundamental change. Translators must be aware of these linguistic nuances to avoid misinterpretation.
- Accuracy
Accuracy is paramount in the translation process, and it is directly affected by the translator's ability to navigate change effectively. Translators must strive to convey the intended meaning of the source text accurately, while also considering the cultural and linguistic nuances of the target language. By carefully considering the changes that may occur during the translation process, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations.
- Comprehensibility
Comprehensibility is another important aspect of translation, and it is closely linked to the concept of change. Translators must ensure that the target audience can easily understand the translated text. This may involve making changes to the source text to make it more accessible to the target audience. For example, a translator may simplify the language or provide additional context to make the translation more comprehensible.
These four facets of change - cultural context, linguistic nuances, accuracy, and comprehensibility - are all essential considerations in the reflection meaning in Kannada. By carefully considering these factors, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the message to the target audience.
3. Meaning Shift
In the context of "reflection meaning in Kannada," meaning shift refers to the subtle changes in meaning that can occur when a word or phrase is translated from one language to another. These shifts can be influenced by cultural differences, linguistic nuances, and the translator's interpretation of the source text.
- Cultural Context
Cultural context plays a significant role in shaping the meaning of words and phrases. When translating from English to Kannada, translators must be aware of the cultural differences between the two languages to avoid misinterpretation or offense. For example, the English word "reflection" may have different connotations in different cultures. In some cultures, it may refer to a thoughtful consideration of an idea or experience, while in other cultures, it may refer to a physical reflection or image. Translators must carefully consider the cultural context of the source text to ensure that the translation accurately conveys the intended meaning.
- Linguistic Nuances
Linguistic nuances also contribute to meaning shift in translation. Different languages have their own unique grammatical structures, idioms, and expressions. Translators must be familiar with the linguistic nuances of both the source and target languages to ensure that the translation is both accurate and natural-sounding. For example, the English word "reflection" can be translated to "" (parivartane) in Kannada. However, the Kannada word carries a slightly different connotation, implying a more profound or fundamental change. Translators must be aware of these linguistic nuances to avoid misinterpretation.
- Translator's Interpretation
The translator's interpretation of the source text can also lead to meaning shifts. Translators must carefully consider the context and tone of the source text to ensure that their translation accurately reflects the intended message. For example, a translator may choose to use a more formal or informal tone in the translation, depending on the context of the source text. This can lead to subtle changes in meaning, as different words and phrases may have different connotations in different registers.
Meaning shift is a complex and challenging aspect of translation. However, by carefully considering the cultural, linguistic, and contextual factors involved, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the intended message.
4. Cultural Context
Cultural context plays a pivotal role in shaping the meaning and interpretation of language. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately. Cultural context encompasses a wide range of factors, including social norms, values, beliefs, traditions, and history.
- Values and Beliefs
Values and beliefs are deeply ingrained in a culture and influence how its members perceive and interpret words and phrases. For example, the concept of "reflection" may have different connotations in different cultures. In Western cultures, reflection is often associated with introspection and self-awareness. However, in Eastern cultures, reflection may be more closely tied to spiritual practices and the concept of karma.
- Social Norms
Social norms dictate acceptable and unacceptable behavior within a culture. These norms can influence the way that words and phrases are used. For example, in some cultures, it is considered impolite to speak directly about certain topics, such as death or illness. Translators must be aware of these social norms to avoid causing offense or misinterpretation.
- Traditions and Customs
Traditions and customs are passed down from generation to generation and can have a significant impact on the way that language is used. For example, in some cultures, there are specific words and phrases that are used during religious ceremonies or festivals. Translators must be familiar with these traditions and customs to ensure that their translations are accurate and respectful.
- History
History shapes a culture's values, beliefs, and traditions. It is important for translators to have a basic understanding of the history of the cultures involved in the translation process. This knowledge can help translators to avoid making mistakes that could be offensive or inaccurate.
By carefully considering the cultural context of both the source and target languages, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the intended message.
5. Linguistic Nuances
In the realm of translation, linguistic nuances play a crucial role in capturing the essence and meaning of words and phrases. When translating from English to Kannada, it is imperative to consider the intricate linguistic nuances of both languages to convey the intended message accurately. Linguistic nuances encompass the subtle variations in grammar, syntax, and vocabulary that can significantly alter the meaning of a word or phrase.
One of the key linguistic nuances that translators must navigate is the difference in grammatical structures between English and Kannada. For example, English sentences typically follow a subject-verb-object structure, while Kannada sentences often follow a subject-object-verb structure. This difference can lead to confusion or misinterpretation if not handled carefully during translation.
Another important linguistic nuance to consider is the use of idioms and colloquialisms. Idioms are phrases or expressions that have a figurative meaning that cannot be understood from the literal meaning of the individual words. Colloquialisms are informal expressions that are commonly used in everyday speech. Translators must be familiar with the idioms and colloquialisms of both languages to ensure that they are translated accurately and naturally.
Understanding linguistic nuances is essential for effective translation, as it allows translators to convey the intended meaning of the source text while also producing a translation that sounds natural and fluent in the target language. By carefully considering the linguistic nuances of both languages, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the message to the target audience.
6. Accuracy
In the context of "reflection meaning in Kannada," accuracy refers to the faithfulness and correctness of the translation. When translating from English to Kannada, it is crucial to convey the intended meaning of the source text accurately while also adhering to the grammatical and stylistic conventions of the target language. Accuracy is a fundamental component of effective translation, as it ensures that the message is communicated clearly and without distortion.
Translators must possess a deep understanding of both the source and target languages to achieve accuracy in translation. This includes a mastery of grammar, vocabulary, and idioms. Translators must also be aware of the cultural context of both languages to avoid misinterpretations or misunderstandings. By carefully considering the nuances of both languages, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the intended message.
Accuracy is particularly important when translating sensitive or technical documents, where even a minor error could have serious consequences. In such cases, translators must take extra care to ensure that the translation is accurate and error-free. Translators can also utilize tools such as translation memory software to improve accuracy and consistency in their translations.
In conclusion, accuracy is a cornerstone of effective translation, as it ensures that the intended meaning of the source text is conveyed clearly and correctly in the target language. By carefully considering the nuances of both languages and utilizing appropriate tools, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that meet the needs of the target audience.
7. Comprehensibility
Comprehensibility plays a crucial role in "reflection meaning in Kannada" as it ensures that the translated text is easily understood by the target audience. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the linguistic and cultural differences between the two languages to convey the intended message accurately and comprehensibly.
Comprehensibility is directly linked to the effectiveness of translation. A translation that is not comprehensible fails to communicate the intended meaning and can lead to misinterpretation or confusion. Translators must, therefore, strive to create translations that are clear, concise, and accessible to the target audience.
To achieve comprehensibility in translation, several factors must be considered. Firstly, translators must have a deep understanding of both the source and target languages. This includes a mastery of grammar, vocabulary, and idioms. Secondly, translators must be aware of the cultural context of both languages to avoid misinterpretations or misunderstandings. Thirdly, translators must carefully consider the intended audience for the translation and tailor the language and style accordingly.
In summary, comprehensibility is a key component of "reflection meaning in Kannada" as it ensures that the translated text is easily understood by the target audience. Translators must, therefore, strive to create translations that are clear, concise, and accessible to the target audience by considering the linguistic and cultural differences between the two languages and the intended audience for the translation.
8. Preservation of Meaning
In the context of "reflection meaning in Kannada," preservation of meaning refers to the ability of a translation to convey the intended message of the source text accurately and effectively. When translating from English to Kannada, it is essential to consider the cultural and linguistic nuances of both languages to ensure that the meaning of the source text is not lost or distorted in the translation process.
- Accuracy
Accuracy is a crucial aspect of preservation of meaning. Translators must strive to convey the intended meaning of the source text as faithfully as possible, without adding or omitting any information. This requires a deep understanding of both the source and target languages, as well as the cultural context of both cultures.
- Comprehensibility
Comprehensibility is another important factor in preservation of meaning. The translated text should be easy for the target audience to understand, even if they are not familiar with the source language. This requires translators to use clear and concise language, and to avoid using idioms or cultural references that may not be understood by the target audience.
- Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is essential for preserving the meaning of a text, especially when translating between languages from different cultures. Translators must be aware of the cultural context of both the source and target languages to avoid making mistakes that could be offensive or misleading.
- Translator's Interpretation
The translator's interpretation also plays a role in preservation of meaning. Translators must carefully consider the context and tone of the source text to ensure that their translation accurately reflects the intended message. This requires translators to have a deep understanding of both the source and target languages, as well as the cultural context of both cultures.
By carefully considering these factors, translators can produce accurate and meaningful translations that effectively convey the intended message of the source text. Preservation of meaning is essential for effective communication, and it is a key component of "reflection meaning in Kannada."
FAQs on "Reflection Meaning in Kannada"
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions about the meaning of "reflection" in the context of English-to-Kannada translation. It provides clear and informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the significance of considering cultural context when translating "reflection" from English to Kannada?
Answer: Cultural context is crucial because the concept of "reflection" may carry different connotations and nuances in different cultures. Understanding the cultural context helps translators convey the intended meaning accurately and avoid misinterpretations.
Question 2: How does linguistic nuance impact the translation of "reflection"?
Answer: Linguistic nuance refers to the subtle variations in grammar, vocabulary, and idioms between languages. Translators must be aware of these nuances to ensure that the translation of "reflection" sounds natural and fluent in Kannada, while still conveying the intended meaning.
Question 3: What is the role of accuracy in translating "reflection"?
Answer: Accuracy is paramount in translation to ensure that the meaning of the source text is conveyed correctly. Translators must have a deep understanding of both English and Kannada to produce accurate translations that faithfully reflect the intended message.
Question 4: Why is comprehensibility important in the translation of "reflection"?
Answer: Comprehensibility ensures that the translated text is easily understood by the target audience. Translators must use clear and concise language, avoiding idioms or cultural references that may be unfamiliar to Kannada speakers.
Question 5: How can translators preserve the meaning of "reflection" in translation?
Answer: Translators can preserve meaning by considering the cultural context, linguistic nuance, accuracy, and comprehensibility of the translation. They must carefully interpret the source text and use appropriate language to convey the intended message effectively.
In summary, understanding the cultural, linguistic, and contextual factors involved in translating "reflection" is essential for effective communication. By considering these factors, translators can produce accurate, comprehensible, and meaningful translations that convey the intended message.
Transition to the next article section:
Next Section: Importance and Benefits of TranslationConclusion
In the realm of language translation, understanding the meaning of "reflection" in the context of English to Kannada is crucial for effective communication. This article has explored the various facets of "reflection meaning in Kannada," emphasizing the significance of cultural context, linguistic nuance, accuracy, comprehensibility, and preservation of meaning.
Translators must carefully navigate the intricate tapestry of cultural and linguistic differences between English and Kannada to convey the intended message accurately. By considering the nuances of both languages, translators can produce translations that not only reflect the surface meaning of words but also capture the deeper cultural and contextual implications.
The ability to translate "reflection" effectively is essential for fostering cross-cultural understanding and communication. It allows individuals and organizations to share ideas, knowledge, and experiences across linguistic and cultural boundaries. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for accurate and meaningful translation continues to grow.
In conclusion, understanding "reflection meaning in Kannada" is a complex and multifaceted endeavor that requires translators to possess a deep understanding of both languages, their cultural contexts, and the nuances of translation. By embracing these principles, translators can produce translations that faithfully convey the intended message and contribute to effective communication across cultures.
You Might Also Like
The Epic Duo: Surya And Vijay Sethupathi's Unforgettable Movie ExperienceMichael Clarke Duncan: A Towering Presence On And Off The Screen
Discover The Latest Movies With Vaga Movies .nl
Meet Michael Che's Wife: All The Details On His Love Life
Everything You Need To Know About Kerry Washington's Husband
Article Recommendations